我々(主語が大きい)は何故MySQLで外部キーを使わないのか
Foreign Key Night
Feb 13th, 2015
Profile

- id: Songmu (ソンムー)
- おそらくはそれさえも平凡な日々 http://www.songmu.jp/riji/
- https://metacpan.org/author/SONGMU
- 趣味はCPANizeです
- はてな チーフエンジニア
- 東京オフィス
- はてなでGoとScala始めました
- Mackerel開発中
最近のCPAN Module
- App::LJ (lj)
- ログからJSONぽいところを見つけて綺麗に出してくれる
- http://www.songmu.jp/riji/entry/2015-02-01-lj.html
Q. 外部キー使ってる人いますか?
Q. 外部キー使ってる人いますか?
- はい僕は使っています
外部キー便利!!!
- MackerelではPostgreSQLで外部キーあり
- そのレコードがあることが保証される
- 各テーブルのidにアプリケーションレベル(Mackerelの場合Scala)で型付けをするとなお便利
- MemberID型、MonitorID型
- → idで誤ったテーブルを引くとかがない
MySQLで外部キーを使わない運用をする理由
それなりの規模のMySQL運用だと外部キーを使用するのをためらう理由がある。
- 使えない機能がある
- パフォーマンス上の理由
- 意図せぬロックを防ぐ
- インデックサイズを抑えたい
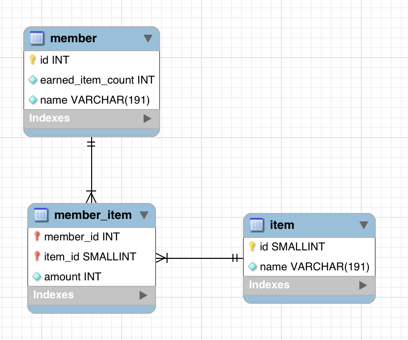
本日のスキーマ
CREATE TABLE `member` (
`id` INTEGER unsigned NOT NULL auto_increment,
`earned_item_count` INTEGER unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`name` VARCHAR(191) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4;
CREATE TABLE `item` (
`id` SMALLINT unsigned NOT NULL,
`name` VARCHAR(191) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4;
CREATE TABLE `member_item` (
`member_id` INTEGER unsigned NOT NULL,
`item_id` SMALLINT unsigned NOT NULL,
`amount` INTEGER unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
CONSTRAINT `member_item_fk` FOREIGN KEY (`item_id`) REFERENCES `item` (`id`),
CONSTRAINT `member_item_fk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`member_id`) REFERENCES `member` (`id`),
PRIMARY KEY (`member_id`, `item_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4;
ERD
パーティションを使えない
http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/partitioning-limitations-storage-engines.html
InnoDB foreign keys and MySQL partitioning are not compatible. Partitioned InnoDB tables cannot have foreign key references, nor can they have columns referenced by foreign keys. InnoDB tables which have or which are referenced by foreign keys cannot be partitioned.
- MySQLはパーティションを設定したテーブルに外部キー制約を加える事が出来ない
- これが個人的には一番大きい
- パーティション切れないとかありえない
暗黙のindex
http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/create-table-foreign-keys.html
MySQL requires indexes on foreign keys and referenced keys so that foreign key checks can be fast and not require a table scan. In the referencing table, there must be an index where the foreign key columns are listed as the first columns in the same order. Such an index is created on the referencing table automatically if it does not exist. This index might be silently dropped later, if you create another index that can be used to enforce the foreign key constraint. index_name, if given, is used as described previously.
- 外部キーと同名のindexが暗黙的に作られるという余計なお世話
- ただし既にそのカラムを使うインデックスがあった場合は作られない
- あとでそのカラムが先頭に来るindexを追加した場合は自動的に消える
- が、別にそっち側のindexいらんやろっていう場合もある (item_idで絞り込む必要ないとか)
- →インデックスサイズ肥大につながるので嫌
リレーション先の行にshared lockがかかる
http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/innodb-locks-set.html
If a FOREIGN KEY constraint is defined on a table, any insert, update, or delete that requires the constraint condition to be checked sets shared record-level locks on the records that it looks at to check the constraint. InnoDB also sets these locks in the case where the constraint fails.
- ロック順に気をつけないと簡単にデッドロック作れる
- DEMOがいちりんちゃんと被りそう
削除がやりづらくなる
- デフォルトだとNO ACTIONで、親の削除(itemの削除とか)は出来ない
- ON DELETE SET NULL/CASCADEは厳しい
- 一斉に大量の更新/削除が走るのはWebサービスでは現実的ではない
- リストパーティションを切ってDROP(or EXCHANGE) PARTITIONとかやるのが現実的
- item_idでパーティション切るとか
- ただしパーティションは外部キー使ってると(ry
- 論理削除は嫌
- 論理削除するにしてもnull埋めとか、0埋めとかそういうことやりづらい
テストfixtureを準備するのがめんどくさい(?)
- これは別にそんなこと無い
- どっちにしても一括で一連のデータを作ってくれるテスト用のヘルパを作るので同じ
- 外部キーを使うとテスト工数が増えるというのは嘘
- 外部キー制約を使わないんだったら逆に丁寧にfixtureを用意した方がいい
- リレーションに不整合がないかはテストで担保する
- 外部キー使わないほうが逆にテスト工数はかかる
まとめ
- 外部キー制約は便利だけどそこそこの規模のMySQL運用では使えない理由がある
- パーティションを使えない
- リレーションの親テーブルをうっかりshared lockしていることがある
- 暗黙のindexが作られて不可避なのでindexサイズ肥大で困る
- ON DELETE CASCADEとか現実的じゃないので制約外したい
- やるにしてもリストパーティション切ってDROPとかしたい
- テストのfixtureを用意するのがめんどくさいってのはそんなことはない。テストしっかり書こう
We are Hiring
- はてなではエンジニアを募集しています
- 東京でも絶賛採用中
- エンジニアは少ない
- 僕が入社後にエンジニア倍増 (2人)
- 東京オフィス自体には30人くらいいます
- もちろん京都にもおいでやす

